场景假设
什么是分布式ID呢? 国家要每天的出生婴儿要发放身份证,为了保证每个地区每天出生的每个新生儿的身份证号码是唯一的。身份证号码就是分布式ID。
主要实现功能:
- 分布式项目获取ID唯一
- 实现高可用及动态扩展
- 如何压榨服务器资源
一、 如何保持 ID 的唯一
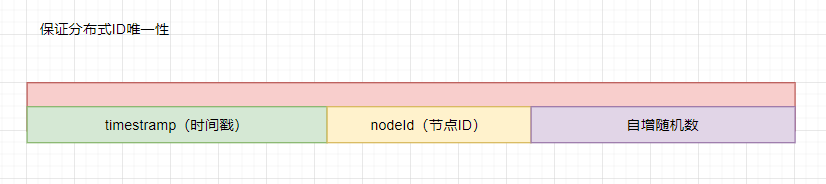
确定得到得主键ID是全局唯一需要保证ID含有这些要素:
- 时间戳,在单个节点中全局唯一且自增
- 节点ID,当应用服务作负载均衡得时候,每个服务有分发不唯一得ID
- 自增随机数,根据业务需求量调整
解释:
节点ID在集群环境是全局唯一的;时间戳在每个节点中是唯一的,是局部唯一的;自增随机数为自增数,则为业务场景递增数;满足这三个条件才可以成为分布式ID;
二、生成分布式ID的流程
2.1 架构图
- IDGen-service 为分布式ID服务
- NGINX 支持服务横向扩展
- zookeeper 主要完成三个功能:
业务主键注册(记录每种业务的自增数最大记录),分发服务的 nodeId(保证每个服务的nodeId不一致) 和每个节点的时钟校验(防止服务发生时钟回拨)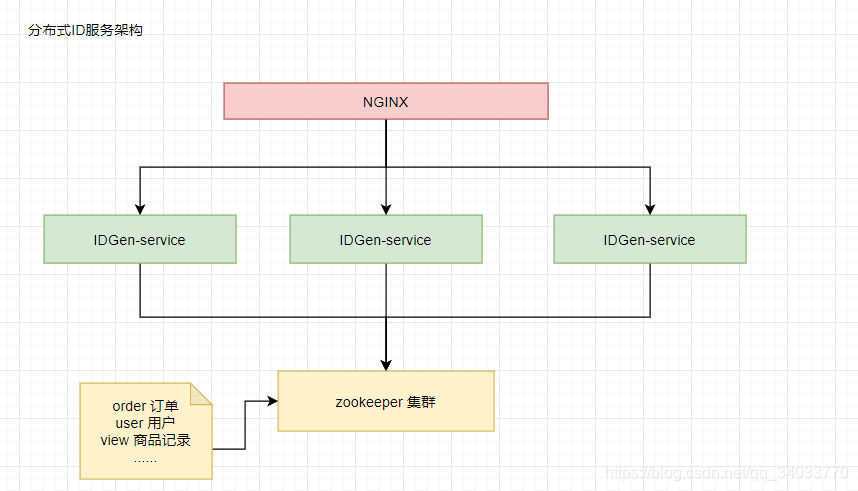
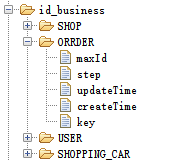
2.2 业务参数组件
上一点说到,每种业务都需要注册到 zookeeper 中,主要包含这几个参数: - maxId 最大的自增数
- step 步长,ID并不会每需要一个生成一个,服务中会有ID池,步长则是ID池的容量
- time 更新时间和创建时间,当不同的节点申请同一个业务资源时,申请完成后更新时间;创建时间则是个记录而已
- key 表示用于不同业务的标识
2.3 ID 缓存对象
ID-Gen 接口实现:1
2
3
4
5
6
7public interface IDGen {
/**
* @Param
* key 业务id
* */
String get(String key);
}
从cache中获取对应的业务主键,没有则不支持这个业务生成主键;cache中每个业务key的操作要保证原子性。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17/**
* 业务key的 JVM 缓存
* */
private final Map<String, SegmentBuffer> cache;
public String get(String businessId) {
if (cache.containsKey(businessId)) {
SegmentBuffer buffer = cache.get(businessId);
// 获取id的原子操作,锁住该业务
synchronized (buffer) {
// segmentBuffer 更新 zookeeper 持久化数据
return this.getIdFromBufferPool(buffer);
}
}
throw new ServiceErrorException("service zk 并没有该业务组件主键");
}
buffer 对象(含ID池,以及生产ID的策略,以及对该资源操作的锁 lock)
- setIdInPool 方法在项目初始化时,会设置 step 长度的线程池
- bufferQueue 队列就是新的ID池,在加载的时候要注意对zk资源加锁并更新
- idPool 为当期对象的 id 池,当id池达到某个阈值是可以往
bufferQueue加入新的 ID1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122public class SegmentBuffer {
public void init(){
this.nextBufferIsReady = false;
this.lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
this.threadRunning = new AtomicBoolean(false);
/*
* 设置 id 池
* */
this.setIdInPool();
}
/***
* buffer 队列,用完一个,下一个接着
* */
private Queue<SegmentBuffer> bufferQueue;
/**
* id 池
*/
private Queue<String> idPool;
public int getPoolSize() {
return idPool.size();
}
/**
* buffer组,预加载的buffer (多线程加入就不会影响该对象的速度)
*/
private SegmentBuffer[] segments;
/**
* 下一个id池 是否已完成加载
*/
private volatile boolean nextBufferIsReady = false;
/**
* zk 记录参数
*/
private String key;
private Long step;
private Long maxId;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
/**
* 当前使用到的id
*/
private static volatile AtomicInteger currentIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
/***
* 当前最大的 id
* */
private static volatile AtomicReference<String> currentIdString = new AtomicReference<>();
/**
* 获取 id 时加锁,只有一个线程能获取到 id
*/
private ReadWriteLock lock;
/***
* 线程是否在运行中
* */
private AtomicBoolean threadRunning;
/**************
* 生成策略相关
* **
* */
/**
* 节点id
*/
private Long serverNodeNumber = 0L;
private Long nowTimeStamp() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* id 生成策略
* (算法还再考虑,策略模式导入方法, 策略类 + 实现 )
*/
private IdGenStrategy idGen;
/***
* 需的参数:
* - 时间戳(nowTimeStamp) + 分发的节点随机数(serverNodeNumber) + 当前数字(currentIndex)
* */
public void setIdInPool() {
idPool = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
bufferQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
CommonThreadUtil.execute(() -> {
for(int i = 0; i < step; i++) {
if (Objects.isNull(idGen)) {
throw new IdCreateErrorException("id 的生成策略为空");
}
String nowId = idGen.createId(nowTimeStamp(), serverNodeNumber, currentIndex.getAndIncrement());
idPool.add(nowId);
currentIdString.set(nowId);
}
});
}
/**
*
* */
public void setNewSegmentBufferInQueue(SegmentBuffer buffer) {
bufferQueue.add(buffer);
this.nextBufferIsReady = true;
}
public boolean hasNextId() {
return !idPool.isEmpty();
}
public String nextId() {
return idPool.poll();
}
}
2.4 业务 ID 的预加载
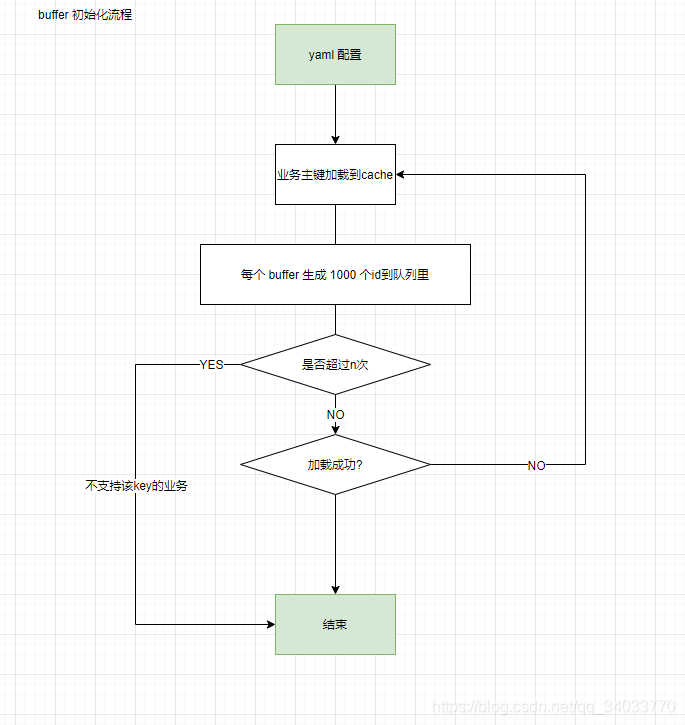
businessKeys 是配置在 yaml 的配置的节点信息,在这种设置的同时会有一个动态拓展业务key的问题,但可以通过新的集群加入新的 key 承载新的业务,使用同一个 zk集群 是不冲突的。
1 |
|
2.5 获取 ID 的主流程
主流程图: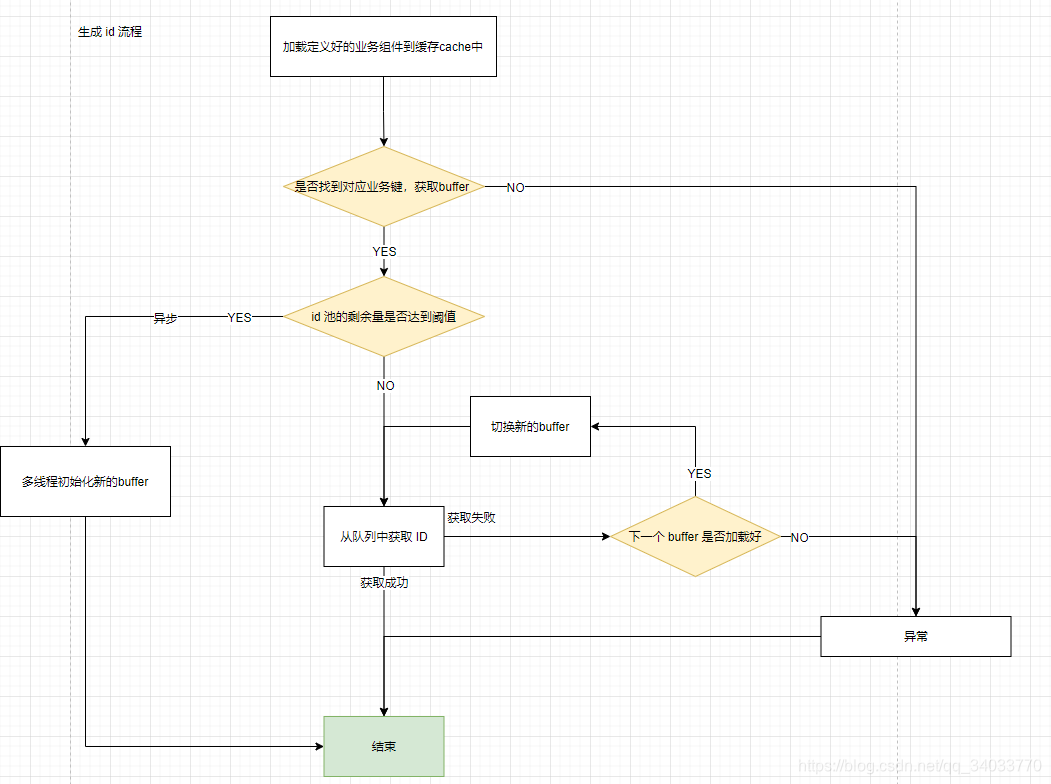
三、如何压榨服务器流程
- 对象的锁要细粒度化
- 只对业务资源锁,然后使用多线程完成剩余的代码逻辑
- 使用无锁来优化代码,无锁能提高效率,却消耗服务器资源
终: 优化点,如何提高分布式ID的并发量
- 优化业务参数(ID池的容量与下一个ID池的加载阈值)
- 启动多线程加载新的线程池(待解决问题,新的ID池加载完成前,ID池已空)
你的支持是我加班的动力
微信
 支付宝
支付宝

微信
 支付宝
支付宝


...
...
00:00
00:00
This is copyright.